此文待重构
简介
队列,又称为伫列(queue),是先进先出(FIFO, First-In-First-Out)的线性表。在具体应用中通常用链表或者数组来实现。队列只允许在后端(称为rear)进行插入操作,在前端(称为front)进行删除操作。
特点
- 队列是一种线性结构
- 相比数组,队列中允许的操作为数组的操作子集
- 只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素
- 队列是一种先进先出(FIFO,First In First Out)的数据结构
操作
队列数据结构使用两种基本操作::
- 进队(enqueue):将数据从队尾插入,队列元素加 1
- 出队(dequeue):将数据从队首移出,队列元素减 1
图示
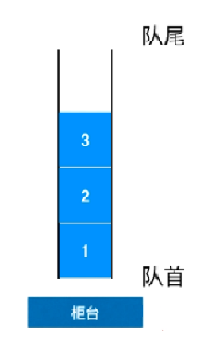
队列类似日常排队一样,人们遵守规则,后来的人排最后,不能插队,队首的人事情办好则出队。
类别
- 顺序队列:在顺序队列中,出队操作后又进行入队操作,当队尾指针已经到数组的上界,不能再有入队操作,但其实数组中还有空位置,存在“假溢出”现象(如下图),解决假溢出的途径—-采用循环队列
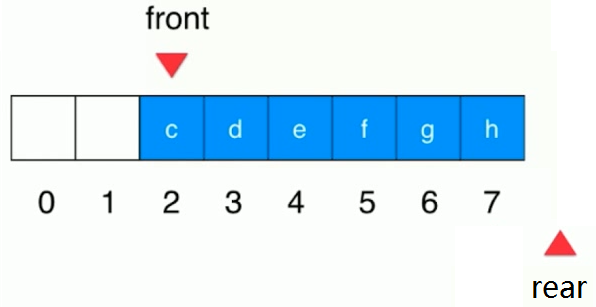
- 循环队列:
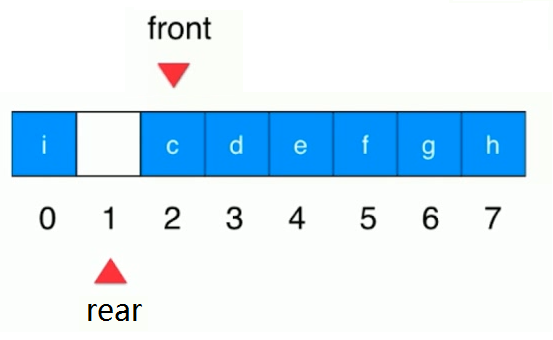
- 臆想成环:
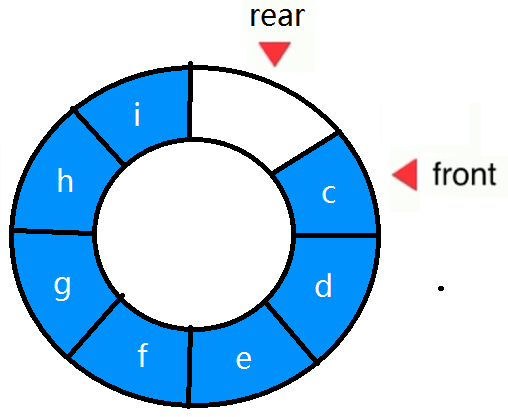
在循环队列中,空队特征是front = rear, 队满时也会有front = rear,判断条件将出现二义性。
解决方案有三种:
- 加设标志位,让删除动作使其为1,插入动作使其为0, 则可识别当前front == rear;
- 使用一个计数器记录队列中元素个数(即队列长度)
- 人为浪费一个单元,令队满特征为 front = (rear +1)%length(数组长度)—空闲单元法
这里采用空闲单元法解决二义性问题。
代码实现(循环队列)
接口定义:
1 | public interface Queue<E> { |
为了使该队列能动态增减,加入以下优化:
1 | //队列扩容 |
enqueue优化:
1 | //元素入队尾 |
dequeue优化:
1 | //元素出队首 |
测试代码
1 |
|
测试结果
1 | Queue size = 1,capacity = 10 |
时间复杂度分析
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| void enqueue(E) | O(1) 均摊 |
| E dequeue() | O(1) 均摊 |
| E getFront() | O(1) |
| int getSize() | O(1) |
| boolean isEmpty() | O(1) |
基于堆的优先队列
请了解堆后再看后续代码,在后续章节有说明(八)数据结构之堆
1 | public class PriorityQueue<E extends Comparable<E>> implements Queue<E> { |
文章信息
| 时间 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 2018-12-02 | 初稿 |